어텐션 모델
어텐션의 기본 아이디어는
디코더에서 출력 단어를 예측하는 매 시점(time step)마다,
인코더에서의 전체 입력 문장을 다시 한 번 참고한다는 점이다.
단, 전체 입력 문장을 전부 다 동일한 비율로 참고하는 것이 아니라,
해당 시점에서 예측해야할 단어와 연관이 있는 입력 단어 부분을
좀 더 집중(attention)해서 보게 된다.
딥러닝 모델이 벡터 Sequence 중에서 가장 중요한 벡터에 집중하도록 하는 모델이라 할 수 있다.
어텐션 모델의 Output은 중요한 벡터를 위주로 나타나기 때문에 Sequence의 중요한 부분에 집중한다고 볼 수 있다.
어텐션 모델은 개념적으로 아래와 같이 동작한다.
- 입력으로 들어온 벡터들의 중요도/유사도를, 현재 state를 고려하여 구한다.
- 각각의 중요도를, 총 합이 1이 되는 상대값으로 바꾼다(소프트맥스 함수).
- 상대값 중요도를 가중치로 보고, Sequence에 있는 벡터들을 가중치합한다.

Attention LSTM 예제
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
TIME_STEPS = 20
INPUT_DIM = 2
def attention_3d_block(inputs):
# inputs.shape = (batch_size, time_steps, input_dim)
input_dim = int(inputs.shape[2])
a = tf.keras.layers.Permute((2, 1))(inputs) # same transpose
#a = tf.keras.layers.Reshape((input_dim, TIME_STEPS))(a)
# this line is not useful. It's just to know which dimension is what.
a = tf.keras.layers.Dense(TIME_STEPS, activation='softmax')(a)
a_probs = tf.keras.layers.Permute((2, 1), name='attention_vec')(a)
output_attention_mul = tf.keras.layers.multiply([inputs, a_probs])
#output_attention_mul = merge([inputs, a_probs], name='attention_mul', mode='mul')
return output_attention_mul
def model_attention_applied_after_lstm():
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(TIME_STEPS, INPUT_DIM,))
lstm_units = 32
lstm_out = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(lstm_units, return_sequences=True)(inputs)
attention_mul = attention_3d_block(lstm_out)
attention_mul = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(attention_mul)
output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(attention_mul)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=[inputs], outputs=output)
return model
def model_attention_applied_before_lstm():
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(TIME_STEPS, INPUT_DIM,))
attention_mul = attention_3d_block(inputs)
lstm_units = 32
attention_mul = tf.keras.layers.LSTM(lstm_units, return_sequences=False)(attention_mul)
output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(attention_mul)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=[inputs], outputs=output)
return model
def get_data_recurrent(n, time_steps, input_dim, attention_column=10):
x = np.random.standard_normal(size=(n, time_steps, input_dim))
y = np.random.randint(low=0, high=2, size=(n, 1))
x[:, attention_column, :] = np.tile(y, input_dim)
return x, y
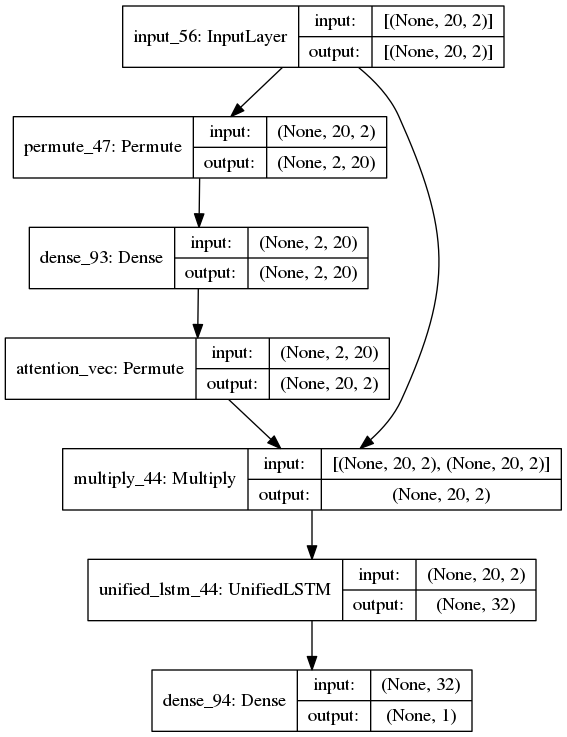
model_attetion_applied_after_lstm()의 모델 구조는 다음과 같다.
여기서 tf.kears.layers.Permute()는 transpose과 비슷한 역할을 한다.
Input Matrix를 transpose()하는 이유는
각각의 Sequence의 벡터 $ y_{i} $에 $ W_{y}$ 행렬을 내적한 값을 더하는 것을 Dense layer로 구현하기 위해서이다.

데이터를 생성하고 모델을 만든다.
모델에서 attention_vec의 출력을 보기 위해서 activation_model을 만든다.
train_x, train_y = get_data_recurrent(300000, TIME_STEPS, INPUT_DIM)
#modelman = model_attention_applied_before_lstm()
modelman = model_attention_applied_after_lstm()
modelman.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
modelman.fit([train_x], train_y, epochs=1, batch_size=128, validation_split=0.1)
layer_outputs = [layer.output for layer in modelman.layers if layer.name == 'attention_vec']
activation_model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=modelman.input, outputs=layer_outputs)attention_vector를 출력해본다.
attention_vectors = []
for i in range(50):
test_x, test_y = get_data_recurrent(1, TIME_STEPS, INPUT_DIM)
predict_output = activation_model.predict(test_x)
#print(predict_output.shape)
dols = np.mean(predict_output, axis=2).squeeze()
#print(dols,"DOLS",dols.shape)
assert (np.sum(dols) - 1.0) < 1e-5
#attention_vectors.append
attention_vectors.append(dols)
attention_vector_final = np.mean(np.array(attention_vectors), axis=0)
pd.DataFrame(attention_vector_final, columns=['attention (%)']).plot.bar()
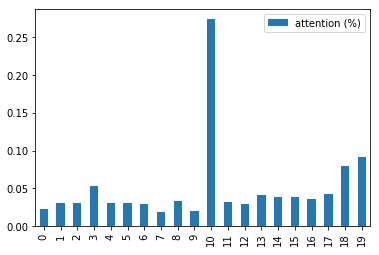

10번 인덱스의 가중치 값이 가장 높다.
RNN의 Long-Term Dependency 해결
Long-Term Dependency(장기 의존성)
제공된 데이터와 배워야 할 정보의 입력 차이(Gap)가 큰 경우 두 정보의 문맥을 연결하기 어려운 현상.
이를 해결하기 위한 방법들은 다음과 같다.
LSTM(Long Short Term Memory Network) 등을 활용하여 해결할 수 있다.
Attention Mechanism을 이용하면 Sequence가 길더라도 그 중에서 중요한 벡터에 집중할 수 있으므로, Long-Term Dependency를 해결할 수 있음.
https://github.com/philipperemy/keras-attention-mechanism
philipperemy/keras-attention-mechanism
Attention mechanism Implementation for Keras. Contribute to philipperemy/keras-attention-mechanism development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
https://github.com/BD-SEARCH/MLtutorial/wiki/Attention-Network
BD-SEARCH/MLtutorial
Machine Learning 개념 정리! Wiki 참고. Contribute to BD-SEARCH/MLtutorial development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
위키독스
온라인 책을 제작 공유하는 플랫폼 서비스
wikidocs.net
'머신러닝과 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 어텐션 메커니즘(Attention Mechanism)의 이해 (0) | 2020.01.10 |
|---|---|
| 케라스 어텐션 메커니즘(Keras Attention Mechanism) (Dense) (1) | 2020.01.08 |
| ConvNet 학습 시각화 (히트맵 시각화) (0) | 2020.01.07 |
| ConvNet 학습 시각화 (중간층 출력의 시각화) (0) | 2020.01.07 |
| 패딩(Padding)과 스트라이드(Strides)와 풀링(Pooling) (0) | 2020.01.07 |